Start ENTRESTO® today to help your symptomatic chronic HFrEF patients feel better and improve their lives vs ACEi (enalapril)1,2^
Most patients with heart failure report limitations in their daily activities due to physical symptoms such as dyspnoea, fatigue, oedema, sleeping difficulties and chest pain.3
^In Ireland, criteria for reimbursement approval of ENTRESTO® applies
Starting ENTRESTO can lead to substantial improvements in social and physical activities comparable to feeling 9 YEARS YOUNGER vs ACEi (enalapril):*1
Sexual relationships
Hobbies & recreation
Household chores
Gardening
ENTRESTO improves how patients feel vs ACEi (enalapril)†2
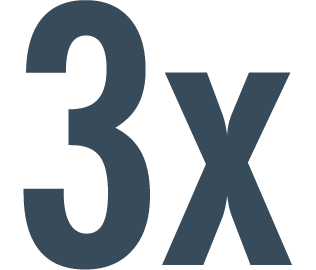
greater improvement in HRQoL as measured by KCCQ‡ overall summary score was experienced by patients taking ENTRESTO§2

HRQoL improvements when taking ENTRESTO vs enalapril, detectable by 4 months after randomisation and sustained throughout 36 months2
ENTRESTO is indicated in adult patients for the treatment of symptomatic chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.9
* As measured by an analysis model that incorporated age and treatment effect. This analysis model was included in a secondary analysis of PARADIGM-HF that examined the effect of ENTRESTO on components of the physical and social limitation section of the KCCQ at 8 months, and longitudinally over 36 months. Patients in the ENTRESTO group had significantly better adjusted change scores in 7 out of 10 physical and social activities vs the enalapril group. The largest improvements over enalapril were in household chores (adjusted change score difference, 2.35 [95% CI, 1.19–3.50], P<0.001) and sexual relationships (adjusted change score difference, 2.72 [95% CI: 0.97–4.46], P=0.002); both persisted through 36 months (overall change score difference, 1.69 [95% CI: 0.78–2.60], P<0.001; and 2.36 [95% CI: 1.01–3.71], P=0.001, respectively).1 PARADIGM-HF was a multinational, randomised, double-blind trial comparing ENTRESTO to enalapril in 8,442 symptomatic (NYHA Class II-IV) HFrEF patients (LVEF ≤40%, amended later to ≤35%). For the primary endpoint, composite of CV death or first HF hospitalisation, ENTRESTO was superior to enalapril (P<0.0001). The median follow-up duration was 27 months.10
† Post hoc analysis of PARADIGM-HF that examined the changes in KCCQ scores at randomisation, Month 4, Month 8, Month 12, and annually thereafter through final visit. 91% of patients enrolled in PARADIGM-HF (n=7,623/8,399) completed the KCCQ at randomisation, with complete data at 8 months for 6,881 patients (90% of baseline). At Month 8, the ENTRESTO group noted improvements in both KCCQ clinical summary score (+0.64 vs -0.29; P=0.008) and KCCQ overall summary score (+1.13 vs -0.14; P<0.001) in comparison to the enalapril group, as well as a significantly smaller proportion of patients with deterioration (≤5 points decrease) of both KCCQ scores (27% vs 31%; P=0.01). Adjusted change scores demonstrated consistent improvements in ENTRESTO vs enalapril through 36 months. Patients who died or did not complete the 8-month KCCQ score were excluded from the principal analysis.2
‡ KCCQ is a self-administered, health-related, QoL measure for HF patients that quantifies physical function, symptoms, social function, self-efficacy and knowledge, and QoL on a scale of 0–100, with higher scores indicating fewer symptoms and physical limitations associated with HF. 7,618 of 8,399 patients from the PARADIGM-HF trial completed the initial KCCQ assessment.2
§ LSM estimation (SE) ENTRESTO vs enalapril: 0.80 (20) vs -0.39 (-0.20). LSM estimates (SE) difference: 1.19 (0.28), P<0.001.2
ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; CI, confidence interval; CV, cardiovascular; HF, heart failure; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; HRQoL, health-related quality of life; KCCQ, Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire; LSM, least squares mean; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NYHA, New York Heart Association; QoL, quality of life; SE, standard error.
References:
- Chandra A, et al. JAMA Cardiol 2018;3(6):498–505.
- Lewis EF, et al. Circ Heart Fail 2017;10(8):e003430.
- Heo S, et al. Heart Lung 2009;38(2):100–108.
- Claggett B, et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373(23):2289–2290.
- Heidenreichet J al. JACC 2022;79(17):e263-e421
- ENTRESTO® Summary of Product Characteristics. Accessed on May 2024 www.medicines.ie.
- McDonagh T, et al. Eur Heart J 2021;42(36):3599-3726.
- McMurray JJ, et al. N Engl J Med 2014;371:993–1004.

