ENTRESTO® replaces ACEi/ARB treatment for heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction with a simple 1 or 2 step titration1


- On low dose ACEi/ARB
- With moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30-60 ml/min/1.73 m2)
- With severe renal impairment† (eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2)
- With moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B Classification)
- With systolic blood pressure 100 mmHg to 110 mmHg
- Dose should be doubled every 3-4 weeks to a target dose of 97 mg/103 mg b.d., as tolerated by the patient


- On high dose ACEi/ARB*
- Dose should be doubled every 2-4 weeks to a target dose of 97 mg/103 mg b.d., as tolerated by the patient

- Target dose, as tolerated by the patient

* No washout needed when switching from an ARB to ENTRESTO®
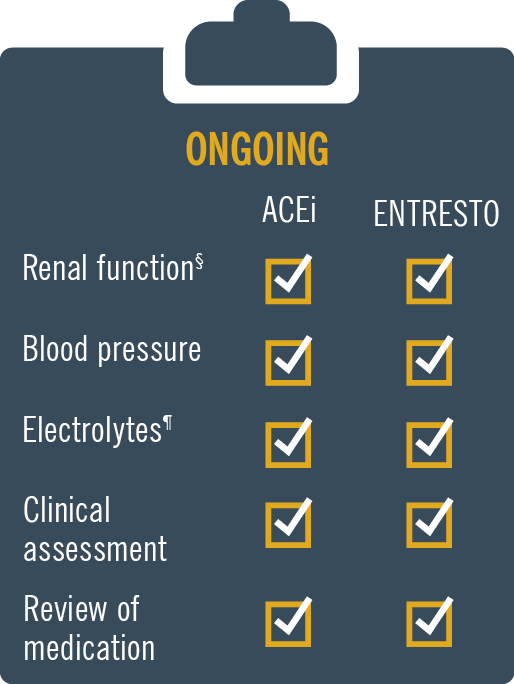
ENTRESTO® has a safety and tolerability profile comparable to enalapril2 MONITORING: Patients on Entresto should be monitored similar to patients on ACE inhibitors and/or ARBs.
* Please refer to individual SmPC of ACE inhibitor / ARB for guidance on current dosing level
† There is very limited clinical experience in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2). Entresto should be used with caution and a starting dose of 24 mg/26 mg twice daily is recommended.1
Prescribe ENTRESTO as your first choice with confidence1
In clinical trials, ENTRESTO generally demonstrated comparable safety and superior efficacy to ACEi (enalapril)1-3
![]()
PARADIGM-HF:* Most commonly reported AEs with ENTRESTO were hypotension, hyperkalaemia and renal impairment1,2
- Fewer patients taking ENTRESTO discontinued therapy due to an AE during the double-blind period: 10.7% vs 12.3% with enalapril2
- While more patients experienced symptomatic hypotension with ENTRESTO than with ACEi (enalapril), there was no increase in the rate of discontinuation due to hypotension-related effects (0.9% vs 0.7%; P=0.38)2
![]()
PIONEER-HF:†
- ENTRESTO showed significantly greater reductions in NT-proBNP and exploratory clinical outcomes, with comparable safety vs ACEi (enalapril), when initiated in hospital following haemodynamic stabilisation after an ADHF‡3
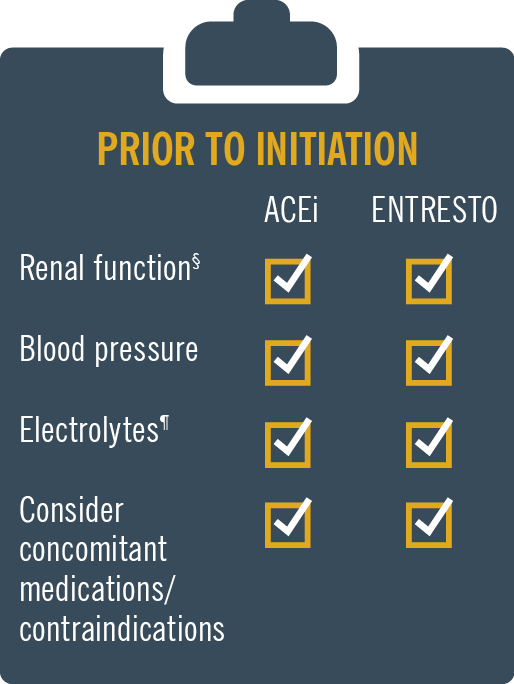

ENTRESTO® (sacubitril/valsartan) is licensed in adult patients for treatment of symptomatic chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction1
CRITERIA FOR REIMBURSEMENT OF ENTRESTO® (SACUBITRIL/VALSARTAN)
To be eligible for reimbursement patients must meet the following criteria:
- LVEF of ≤35%, and
- Symptomatic (NYHA functional class II - IV) and
- Receiving stable dose of ACE inhibitor or an ARB prior to initiation of Entresto®
- Systolic blood pressure ≥100mmHg
- Serum potassium (K+) ≤5.4mmol/L
- Starting dose of Entresto®
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR REIMBURSEMENT APPROVAL OF ENTRESTO®
Please provide the below supporting information where available:
- Current heart failure medications
- Demographics - gender, age
- Laboratory tests, where available
Starting Entresto®:
Entresto® contains valsartan and therefore should not be co-administered with another ACEi or ARB containing product1
For patients previously on an ACEi, stop ACEi for 1.5 days (36 hours) before starting Entresto®1
Monitoring: Patients on Entresto® should be monitored, like patients on an ACE inhibitor and/or ARB.1 For full prescribing information please refer to the SmPC.
ENTRESTO is indicated in adult patients for the treatment of symptomatic chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.1
* PARADIGM-HF was a multinational, randomised, double-blind trial comparing ENTRESTO to enalapril in 8,442 symptomatic (NYHA Class II-IV) HFrEF patients (LVEF ≤40%, amended later to ≤35%). For the primary endpoint, composite of CV death or first HF hospitalisation, ENTRESTO was superior to enalapril (P<0.0001). The median follow-up duration was 27 months.2
† PIONEER-HF was a prospective, multicentre, double-blind, randomised, controlled trial designed to assess the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of in-hospital initiation of ENTRESTO compared with enalapril in 881 adult patients in the United States with HFrEF (EF ≤40% and NTproBNP ≥1600 pg/mL or BNP ≥400 pg/mL) stabilised during hospitalisation for ADHF. The primary endpoint was time-averaged proportional change in NT-proBNP from baseline through Weeks 4 and 8. An exploratory clinical endpoint was the outcome of a composite of serious clinical events, which included death, rehospitalisation for heart failure, implantation of a left ventricular assist device, and inclusion on the list of patients eligible for heart transplantation3
‡ Primary endpoint: Time-averaged proportional change in NT-proBNP concentration from baseline through Weeks 4 and 8.3
ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ADHF, acute decompensated heart failure; AE, adverse event; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; CV, cardiovascular; EF, ejection fraction; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HF, heart failure; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; K+, potassium; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NT-proBNP, N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide; NYHA, New York Heart Association; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
References:
- ENTRESTO® Summary of Product Characteristics. Accessed on May 2024 www.medicines.ie.
- McMurray JJ, et al. N Engl J Med 2014;371:993–1004.
- Velazquez EJ., et al. N Engl J Med 2019; 380:539-548
